Introduction
Definition of Cerebral Palsy (CP) - Today, CP has become very common in children. It is a neurological disorder that is non progressive in nature and lead to causing disorders of movement and posture. It occurs due to insult to immature brain. But the definition needs to be revised. CP can be classified in three categories that are physiological, topographical and etiological (Kakooza-Mwesige, Forssberg and Tumwine, 2015). It consists of different factors such as prenatal, antenatal and postnatal depending on various pathological and physiological factors. In children, CP is identified easily by variables like GMCFS.
Assignment Prime is an online assignment writing service provider which caters the academic need of students.
Get Best Pricing Quotes Free Samples Email : help@assignmentprime.com Order NowCP mostly occurs in childhood due to physical disability. It is important to know epidemiology of CP before finding out its prevalence. According to research conducted, it is observed that CP rates lie in between 2.0 to 2.5 per 1000 births. But, it is elucidated by Australian cerebral palsy register report (ACPR) that rate of CP is 2.1 per 1000 births. Besides this, many studies are done on this and it shows different results. But, Ryan, Forde and Gormley, 2015, argues that CP is not a disease but a simple disorder that occurs due to neuromuscular and musculoskeletal impairments. They lead to static and dynamic instability. The complexity of CP can be identified by understanding its anatomy and physiology of type of CP.
Difficulties in CP - A person suffering from CP may face many difficulties in day to day work. It may put certain restrictions on the person to work. This is because; it makes the person’s physical and mental health weak. The weakness may occur due to various patho physiological factors. Its examples are seizure disorders, hearing and visual problems which include attention defects, emotional issues and musculoskeletal problems.
There are several factors in neuro muscular pathology in CP. It has effects on the physical health of child. Shortening of muscle in one. In a research, it was found that CP children skeletal muscle does not get relaxation during activities (Chiarello, Palisano and Chang, 2016). Due to this, the muscle tone increases. Besides this, there occurs an imbalance in between muscle agonist and antagonists. It also directly effects muscle resulting in bony torsion and instability in weight bearing joints. Thus, there is loss in bone mass due to degenerative arthritis. It forms deformities in CP.
Pathology in neuro muscular is caused by problems in upper neuron lesion. This may lead to several difficulties like loss of selective motor control, depending on primitive reflex patterns, etc. This can lead to rise in other problems. For example – spasticity, fixed muscle contracture, etc.
Some children are not able to walk due to weakness in limbs. GMFCS has developed five ordinary levels to show the process of capacity in CP children (Hirvonen, Ojala, and Tammela, 2014). The levels represent different age groups. Age groups is divided as less than 2 years, 2-4, 4-6 and 6-12 years. Level one children can perform all activities with some difficulty in balance and coordination. On the contrary, level 5 children faces difficulty in controlling their head, arm, and neck. Hence, GMCFS is highly used in CP population.
CP children are having abnormal muscle tone. It occurs due to body posture or movement disorder. It can have a great impact on body balancing mechanism. CP children also have abnormal muscle endurance as compared to healthy people. The major problem faced by these children are gait disabilities that contain stiffness in knee, crouch gait, etc.
Along with this, there are many health issues that describe CP children. It can be related to nutritional or non-nutritional in nature that causes effects related to neuro growth (Myrhaug, Odgaard-Jensen and Jahnsen, 2017). It is because; children with motor impairment find it difficult to swallow or feed food. This will affect their gastrointestinal function. This is the reason; they spend most of their time in sleeping. This is a sign of neuro growth effect on the children.
It is important to consider non nutritional factors in the growth of child as it can cause abnormalities such as neuro-trophic effects, immobility, etc. It effects joint breadths, limb, etc. Other than this, the outcomes related to child health are intellectual change in cognitive insufficiency. In this, there is no interaction in between mental level and damaged memory. Another major disability is epilepsy that are unprovoked seizures (Cameron, Brousseau and Gannotti, 2018). At times, there is the change in child behaviour. It is because of attention deficits or emotional issues. For example: ASD or ADHD disorders.
Thus, from the above discussion, it can be concluded that CP is motor disorder. It is because of problems associated with it and health results. In this, effective treatment can be given by following interdisciplinary and disciplinary practices. For example – DXA scanning is used to diagnose the bone loss in CP child.
DXA Scanning - It is an X ray absorptiometry that measures various body compositions like bone growth and mass. It also measures bone mineral thickness (BMD) in CP children. As bone grows continuously, it is difficult to interpret the actual bone mineral. Moreover, DXA is a complex process.
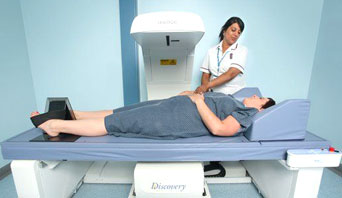
Illustration 1: DXA machine
(Source: National Health Scheme, UK)
Clinical Relevance of DXA
- DXA’s main aim was to use in diagnosis of osteoporosis. But after sometime, it was used in investigating imperative locales of spine, neck and arm. As technology got advanced, DXA was used in many other things (Himmelmann, Horber and KrägelohMann, 2017). It was also used in calculations and investigation of skeleton and other tissues.
- DXA is mainly related to nature of bone loss and problems related to musculoskeletal pathology. So, it is necessary to identify techniques that were used in clinical diagnosis. This can be used during diagnostic procedure of CP child by immobilising it. Moreover, by identifying the pros and cons of techniques, immobilisation effect on CP child can be reduced.
Techniques used during various scanning procedures to Immobilize children with Musculo-Skeletal abnormalities
There are various scanning procedures that are used to immobilize child. In this, the cutaneous stimuli of child is maintained to prevent involuntary movements. It is as follows:-
Spinal Immobilization
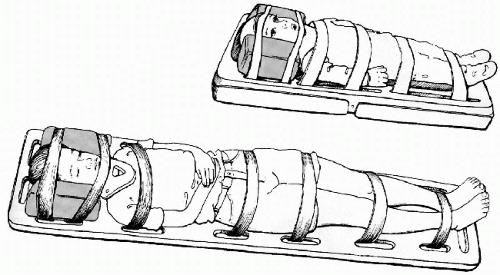
Illustration 2: Spinal Immobilization
(Source: Pediatric cervical spine Injuries)
It is a technique that is applied on children with spinal cord injuries. It consists of spine broad that is very hard. It uses Velcro to immobilise spine, a cervical collar that prevents head from rotating while having a scan. The cervical collar and spine board helps in immobilising child with unstable injuries (Kakooza-Mwesige, Forssberg and Tumwine, 2015). Its advantage is that it eliminates pain making it easier for child to immobile. Its disadvantage is that it can cause artefact that can block the image and results in poor scanning. It will hinder the diagnosis process. Moreover, the spine board is hard in nature that can cause rythma and pain in the body. Also, through this, movement of limb is not prevented.
Whole Body Wrapping (Swaddling)
Illustration 3: Whole body wrapping
In this, the child’s whole body is wrapped. Generally, it is used during MRI. For wrapping the body, blanket or cloth sheet is used. Clips are tied around so that there will be no movement of body. It is a clinical tool which is used for immobilization of spinal at the time of several processes of diagnosis like subluxation, major fractures, dislocation of joints, etc. Sheet is wrapped in clockwise direction covering both upper and lower limbs. Furthermore, head band is used that helps in reducing the noise during MRI. So, this helps in making a child sleep easily. The benefit of using this is that it is less expensive and an effective process. Child can be adjusted in any position by using blanket (Ryan, Forde and Gormley, 2015). It also helps in minimising intra scan motion during MRI. Its disadvantage is that it can wake up child during examination. This will result in repeating the scan. It will incur more expenses. Moreover, it is a time consuming process. This technique is also difficult to be applied on older child.
Vacuum Splint Device
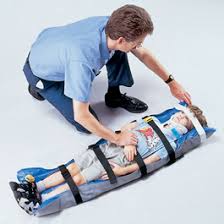
Illustration 4: Vacuum Splint Device
In this immobilisation is given by various procedures like dynamic renogrphy. It contains a torso in which vacuum splint is filled through air valve. Then, torso is secured by using straps and velcro. For securing head, a separate two inch tape is there instead of velcro. After this, air is removed from vacuum splint. Then, splint is molded to head and neck and child is given with manual stabilisation. Its advantage is splint is easy to use and provide comfort to child body. Also, it helps in better and effective immobilisation (Chiarello, Palisano and Chang, 2016). It is a very quick procedure of diagnosis. Disadvantages are head band is very cumbersome to use as it does not provide enough support to head. Sometimes, it provides discomfort to child due to air inflow and outflow. The excessive air can also be a reason for discomfort. Besides this, it can also lead to poor image quality during the scan.
Compression Bandages
Objectives
The bandages are used for immobilization in children and also termed as retention brands. Further, it is known as compression tape because it helps in refraining the child from movement. It is used and connect with table as well as couches from two sides. The effectivess of compression tapes is reflected when medical professionals use it with the help of sandbags.
Benefits
This immobilization tape can be effectively used because it is conventional and not costly in accordance to medication tools (Fonseca Junior and et.al., 2017).
Limitations
Tape creates pressure on child to restrict movement and It has mobility at the time of scan.
Pigg-O-Stat Immobilization Unit

Illustration 5: Compression Bandage (Image Courtesy: Pediatric Radiology)
Objectives
It is a clinical tool which is used by medical practitioners and professionals to refrain child at the time of diagnosis process such as radiography. It is used for x-ray of spine, abdominal and chest for maximum 3 year old child. The position of tool is upright and it comprises manageable Plexiglas sleeves to refrain abdominal and thoracic areas. Further, it has rotating base which make exray process simpler. The seat has two holes where lower limb of child is inserted with raised arms (Gordon, Charles and Wolf, 2015). Further, the sleeves of tool are pushed forward to block abdomen and thorax of children.
Benefits
The diagnioistic professional can adjust machine according to different anatomical position. Moreover, it does not lead to artefacts and therefore, helps in getting quality x-rays (Burkhardt and et.al., 2017).
Limitations
The seat adjustment leads to restless in child due to which he or she may cry which can impact radiography (Eliasson, Krumlinde-Sundholm and Wang, 2015).
Papoose Board
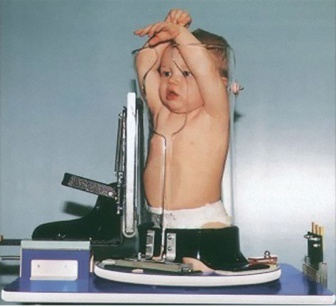
Illustration 6: Fig 8: Pigg-O Stat Immobilization Unit (Image Courtesy: Modernway Immobilizer, Inc, Cliffton, Tenn)
Objectives
The board is used to restrict movement of child at the time of scan. It comprise tape which is of light weight and rigid board. The tapes are area of arm and are diagonal which helps in keeping body shape of child appropriate and restricted. Further, the straps are attached with velcro and flaps which are detachable and even confortable for child. The board also consist of strap which in the head side of child. The position of child is spine and arms are wrapped which restricts movement of children and make scan easy.
Benefits
It is the most effective tool that is used to retract movement of child in case of child incorporation at the time of DXA scan.
Limitations
Generally for parents it is not effective tool because in some case child become restless at the time of securing grip with velcro.
Problems arise during diagnosis with radiologist and scanning professionals
Regardless of advancement in pathological tools, there are various problems faced by technicians and radiologist especially at the time of mobilizing patient. The problems with technician teams are like restlessness, crying, intolerance, reflex patterns, lack of quality due to mobility, incooperations of child, etc. Managing these issue seems general but are hard to manage.
There are various studies which help in determining ways to restrict movement at the time of scan or x-ray. There are various past studies which have derived issue of restraining in clinical practices in diagnostic centre but none of them aimed at deriving ways of managing immobilisation. The major issue which technician faces with clinical setting is DXA that affects spinal or upper limb immobilization which is not related to restraining of whole body. Moreover, retraining techniques also do not go with every child which discomforts family of children and hampers the quality of diagnosis.
Aim
- To ascertain pros and cons of restraining methods which were used in the past studies with diagnostic process afore paediatric group
- To explore new body wrapping tool which can provide alternative solution of handling paediatric group at the time of scan
- To determine effective connection in between restraining and declining ROM
- To assess past research to derive new wrapping technique which owns efficiency to restrain movement of CP child
Methodology
This chapter of research will assist in determining appropriate methods which can be used in project with experimental design. This phase of research is focused on deriving a new way of retraining movement of child and comparing present wrapping tools in diagnostic centres at Liggin’s Institute.
Overview of Experimental Design
The design is considered to be effective as it is focused on deriving possible ways after experiencing certain situation. In this project, the scholar will focus on comparing present wrapping tools used in Liggin’s Institute and will propose new techniques to assist technicians in restraining movement of child during scan. The experiment will be based on primary survey with 10 respondents who are enrolled in study and are in between 5 to 18 years.
Ethical consideration plays a vital role as it helps in increasing the effectiveness of study and aids in maintaining confidentiality of data. Therefore, for this project, scholar will seek approval from committee of health and disability. In addition, the respondents who will assist in experimentation have signed the form of consent where the person has ensured that no one is forced to participate in activity instead process is conducted with consent and interest of all participants.
The scholars signed ethical form with 8 participants. The group that will be involved in experimentation consists of children of 5 to 16 years which will help in deriving movement disorders with both the techniques. Further, it includes aged group that will look for health concerns. The research information is based on previous medical researches and data which is available in Liggin’s Institute. Thus, all respondents involved in experimentation will be informed about current findings which help in determining the effectiveness of their participation.
In this, the participants are agreed with consent on two wrapping tools of centre in which one will be present techniques which is used at Liggin’s Institute and one will be new proposed tool to restrain movement of CP patient. In this experiment, the respondents will face movement of limbs and abdominal which will helps in deriving effectiveness of both the tools. However, both the experiment will be done in one visit of respondents which will help in saving the time and finishing research within time constraints.
The visit of participants will comprise detailed information about them which includes their understanding level, name, age, gender, ethnicity, weight and height.
Current Wrapping Technique Used at Liggin Institute :
A cloth sheet will be placed in bed before lying the child. This will wrap the body of child
After this chidl will be asked to lie in supine position with both arms resting on side of body. Firstly left arm will be immobilised by rolling cloth on left elbow taking cloth under his waist by lifting it up and taking cloth on right side.
Then same end of cloth sheet will be wrapped around abdomen of child from right to left. The sheet will be placed undermeath chid back.
In same way the above procedure is done with right arm.
Proposed Wrapping Technique
The propsed wrapping technique is based on child comfort that is placing bedshhen on clinical setting, making child comfrtable in supline position. Than fisrt professioanl immobilze upper lim of child, wris and than shoulder. Then beddsheet will be placed underneath neck of child which will helps in easy movement of neck. Lower imb will be managed with secnd coth which will wrap kee and hip of child. the wrapping will be abed on time . Motion of limb will be mannual the upper and lower limb comprise Upper limbs and lower limbs comprise Hip flexion,Knee Flexion Shoulder flexion, Shoulder abduction, Elbow flexion, Elbow supination/pronation.
References
- Cameron, R.A., Brousseau, J. and Gannotti, M.E., 2018. Multimodal Community-Based Exercise for Children with Cerebral Palsy: Dosing Interventions for Effectiveness.Critical Reviews™ in Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine,30(1).
- Chiarello, L.A., Palisano, R.J. and Chang, H.J., 2016. Family priorities for activity and participation of children and youth with cerebral palsy.Physical therapy,90(9), pp.1254-1264.
- Himmelmann, K., Horber, V. and KrägelohMann, I., 2017. MRI classification system (MRICS) for children with cerebral palsy: development, reliability, and recommendations.Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology,59(1), pp.57-64.
- Hirvonen, M., Ojala, R. and Tammela, O., 2014. Cerebral palsy among children born moderately and late preterm.Pediatrics, pp.peds-2014.














